By continuing your visit to this site, you accept the use of cookies.
Learn + I agreeRisks

Most of us know that drinking germ-contaminated water implies risks of getting intestinal issues such as abdominal cramps, or diarrhea.
However, we are less aware that there are risks of getting a respiratory tract infection through germs found in water aerosols1.
Where do aerosols come from?
Aerosols are produced by artificial systems containing water such as:
- Hot tub
- Humidifiers or sprayers
- Air conditioners
- Cooling towers
- Drinking water pipes (faucets, shower heads, etc.)
- Fountains with water jets



Microbial overload can become a problem
Water treatment plants produce tightly controlled, high quality drinkable water. This water contains germs which are usually not dangerous for our health. However, formation of biofilms2 can lead to a significant increase in bacteria, and if it is a pathogenic3 bacteria, there is a risk of developing a disease.
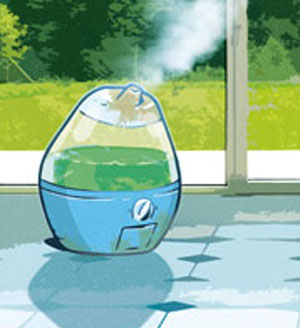
Air conditioning systems or badly maintained humidifiers can contain biofilms and produce aerosols. Legionella pneumophila and Parachlamydia acanthamoebae were discovered during outbreaks caused by aerosols coming from an air conditioning system (Legionella) or a humidifier (Parachlamydia). In water networks, we can often find so called « atypical » mycobacteria4 because they are different from the ones causing tuberculosis5, which are more well-known.
Amoebas: microbial reservoirs
Amoebas are small single-cell organisms living in water. They are only visible by looking through a microscope. The three previously mentioned bacterial species can live and multiply inside amoebas, serving as reservoir for these bacteria.
It is quite likely that a lot of other waterborne germs live in amoebas. Some of them might cause respiratory diseases, especially in people with weak immune systems6, such as kids, pregnant women, transplanted patients and patients undergoing chemotherapy.

Some probably inoffensive new germs found in the water
The microbiology research group lead by Prof. Greub in Lausanne is looking for new germs in aquatic ameobas. He recently found several new bacterial species and even some giant viruses. They were named after the place they were discovered such as Estrella lausannensis, Bosea lausannensis, Lausannevirus or Cedratvirus lausannensis.
For now, these germs seem to be inoffensive towards humans.
Aerosols1 = Water droplets that can be transported by wind and air and enter our respiratory tracts.
Biofilm2 = Community of microbes creating a thin viscous layer.
Pathogenic3 = That causes pain (from the Greek pathos). Therefore, a pathogenic agent is a disease-causing microbe.
Mycobacteria4 = Bacterial family present in the environment (soil, water, food, plants) with a thick outer layer that makes them resistant to many anti-bacterial treatments. Tuberculosis and leprosy are caused by members of this family.
Tuberculosis5 = Infectious disease affecting mostly the lungs, causing cough, fever and weight loss. This disease can reach several other organs such as bones, kidneys and liver. It is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Immune system6 = Set of mechanisms (antibodies, white blood cells…) protecting us from infections.
